About University of Toronto
University of Toronto
Articles by University of Toronto
Translating an Evidence-Based Physical Activity Service From Context To Context: A Single Organizational Case Study
Published on: 28th March, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7286356939
Background: SCI Action Canada partnered with researchers to adapt an evidence-based leisure-time physical activity (LPTA) counselling service (Get-in-Motion (GIM). A satellite GIM service called Passez à l’action was established within a French-speaking context for persons with physical disabilities. An understanding of the determinants that infl uenced the implementation and functioning of the GIM service within the Adaptavie context are required to maximize the potential of other community-based LTPA services being successfully introduced in similar organizations.
Purpose: The case study objectives are to: 1) describe the characteristics and implementation contexts of two leisure-time physical activity counselling services for Canadians with a physical disability and the adoption process that took place when the protocol was translated to a new context, and 2) elucidate, from the point of view of the service providers, the organizational determinants that could have facilitated and/or hindered the implementation and functioning of these services.
Methods: Guided by the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research, focus groups were held with the directors and staff of each service. Mixed-content and thematic analyses were then used to determine overarching themes.
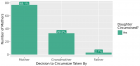
Results: Findings suggest that the presence of service innovators fosters ownership of the service and facilitates ongoing staff training and support. A thoughtful implementation plan should be included as a component of translation between contexts.
Conclusions: Lessons learned and recommendations for future translation of similar evidence-based services to additional contexts are discussed.
Exercise preserves pancreatic β-cell mass and function in obese OLETF rats
Published on: 19th June, 2018
Although exercise has been proposed to be beneficial to type 2 diabetes, its effects on β-cell function and mass remain unclear. In the present study, the effects of long-term swimming training on the function and mass of β-cells in diabetic OLETF rats were examined. At 44 weeks of age after developing diabetes, the OLETF rats were divided into two groups: a control group and an exercise group. The exercise group had a daily swimming for 12 weeks. While not found with the control rats, in the obese OLETF rats, the exercise reduced the weight gain which was associated with improved glucose tolerance and elevated circulating insulin levels as determined by the oral glucose tolerance test and insulin ELISA. The exercise improved plasma total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and also significantly increased the islet β-cell mass and pancreatic insulin content associated with decreased β-cell apoptosis and elevated activation of the serine/threonine kinase, Akt. The present studies suggest that exercise improves diabetes symptoms via enhancement of the β-cell mass and function through decreasing glucolipotoxicity and reducing β-cell apoptosis by activating Akt in obese OLETF rats.
A novel case of an infantile fibrosarcoma-like tumor with KIAA1549-BRAF translocation and an oncogenic NF2p.Q459* SNV with potential clinical significance
Published on: 27th August, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 9272372468
We report a case of a right gluteal mass from the sacroiliac joint to the knee of an infant girl. Biopsy showed histopathological features similar to infantile fibrosarcoma (IFS). However, unlike most IFS, no ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene abnormality was detected. Molecular analysis with TruSight RNA Pan-Cancer Panel detected the presence of KIAA1549-BRAF translocation and an oncogenic NF2p.Q459* SNV with potential clinical significance. A review revealed that the combination of this patient’s tumor site with the presence of a KIAA1549-BRAF translocation abnormality and an accompanying single nucleotide variant has not been previously described. The detection of this translocation abnormality raises the possibility that the spindle cell tumors in infants with an absence of the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene abnormality might have a distinct pathogenetic mechanism different from the previously known IFS and congenital mesoblastic nephroma. Furthermore, the discovery of BRAF translocation and its aberrant signaling of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in this tumor contributes to the promise of clinical benefit of using the MEKi trametinib for the treatment of progressive disease that is refractory to conventional chemotherapy.
A Novel Strategy to Improve Radiotherapy Effectiveness: First-in-Human MR-guided Focused Ultrasound-Stimulated Microbubbles (MRgFUS+MB) Radiation Enhancement Treatment
Published on: 24th August, 2023
Background and aim: Preclinical in vitro and in vivo experiments suggest that radiation-induced tumour cell death can be enhanced 10- to 40-fold when combined with focused-ultrasound (FUS)-stimulated microbubbles (MB). The acoustic exposure of MB in the tumour volume causes vasculature perturbation, activation of the acid sphingomyelinase (ASMase) ceramide pathway, and resultant endothelial cell apoptosis. When the tumour is subsequently treated with radiation, there is increased endothelial cell death and anoxic tumour killing. Here we describe a first-in-human experience treating patients with magnetic resonance (MR)-guided FUS-stimulated MB (MRgFUS+MB) radiation enhancement.Case presentation: A head and neck cancer patient with recurrent disease underwent radiotherapy for 5 separate sites of locoregional disease followed by systemic therapy. The first consisted of a course of 45 Gy in 5 fractions alone, the second of 30 Gy in 5 fractions with hyperthermia, and the three others of 20-30 Gy in 5 fractions along with MRgFUS+MB treatment. The treatment methodology used an MR-coupled FUS-device operating at 500 KHz and 540 kPa peak negative pressure with an insonification time of 750 ms spread over 5 minutes to stimulate intravenously administered MB within tumour target. All sites treated with stimulated MB had a complete radiological response, and subsequently, the patient’s other cutaneous metastatic disease disappeared. The patient has been under surveillance for over two years without active treatment or disease progression.Discussion: MRgFUS+MB was well-tolerated with no reported treatment-related adverse events, which can be attributed to the capability of FUS to selectively stimulate MB within the tumour volume while sparing the surrounding normal tissue. Sustained local control at all target sites aligns with earlier preclinical findings suggesting the radiation enhancement potential of FUS+MB.Conclusion: MRgFUS+MB represents a novel and promising therapy for enhancing radiation efficacy and improving therapeutic index with potential improvements in disease control.
Hospitalization, Surgery and loneliness
Published on: 3rd January, 2024
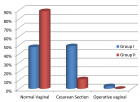
Being hospitalized or undergoing a surgical procedure may be quite an isolating and lonely experience. This review explored loneliness in the hospital and surgical setting, and highlights the emotional and psychological challenges experienced by patients during their healthcare journey. While hospitals traditionally provide medical and surgical care for a wide array of conditions, the irony lies in their potential to disrupt one’s daily routines, contribute to loss of control, prolong hospital stays, and limit connections with family and loved ones leading to negative psychological well-being and intensifying feelings of loneliness. The implications of loneliness in the hospital and surgical contexts are discussed along with recommendations for improving the healthcare system’s response to the negative health consequences associated with loneliness. Coping strategies are discussed, including social support mechanisms, and approaches to healthy behaviors, i.e. mindfulness, which contribute to mitigating loneliness, in the context of hospitalizations and surgery.
Harmonizing Artificial Intelligence Governance; A Model for Regulating a High-risk Categories and Applications in Clinical Pathology: The Evidence and some Concerns
Published on: 18th March, 2024
The Canadian healthcare system, grappling with issues like systemic and intelligently established structural anti-black racism, including indigenous nations; even within Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Communities: and deteriorating outcomes, sees potential in AI to address challenges, though concerns exist regarding exacerbating discriminatory practices. In clinical pathology, AI demonstrates superior diagnostic accuracy compared to pathologists in a study, emphasizing its potential to improve healthcare. However, AI governance is crucial to navigating ethical, legal, and societal concerns. The Royal College of Physicians of Canada acknowledges the transformative impact of AI in healthcare but stresses the need for responsible AI tools co-developed by diverse teams. Despite positive attitudes towards AI in healthcare, concerns about patient safety, privacy, and autonomy highlight the necessity for comprehensive education, engagement, and collaboration. Legal concerns, including liability and regulation, pose challenges, emphasizing the need for a robust regulatory framework. AI application in healthcare is categorized as high-risk, demanding stringent regulation to ensure safety, efficacy, and fairness. A parallel is drawn to drug regulation processes, suggesting a similar approach for AI. The lack of transparency in AI-based decision-making raises ethical questions, necessitating measures to address biases and ensure patient privacy. Social accountability is crucial to prevent AI from exacerbating health disparities and harming marginalized communities. In conclusion, while AI offers potential benefits in clinical pathology, a cautious approach with comprehensive governance measures is essential to mitigate risks and ensure ethical AI integration into healthcare.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."